Household level Grey Water Treatment in Irbid Area in the North of Jordan
Wafaa Ahmed Bakheet
Northern Ghour Supervision Department || Ministry of Education || Jordan
Tab title
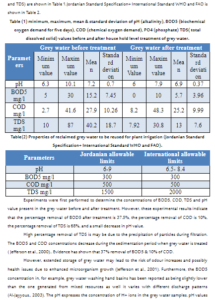
Abstract: One of the means of meeting the water needs in the areas of scarcity is the reuse of grey water generated at the household level. This is water that comes out of the kitchen, bathtubs, washing machines and dishes. The water that coming out of the toilets is black water. This study aims to evaluate the potential of grey water availability in Irbid Area in north of Jordan, by testing and comparing between grey water quality before and after household level treatment using a vertical multi-layer filter of sand and gravel then, reuse it for home gardens. Total grey water generation from different household sources were measured by water meters in five selected household during summer and winter. The physical, chemical and biological analysis of the samples revealed that grey water contains significant levels of suspended solid, chemical &biochemical oxygen demands, and inorganic compounds. Statistical analysis results indicated that there is a various removal percentage of the above parameters. Experimental results indicate that the percentage removal of BOD5 is 37.5%, the percentage removal of COD is 10%, the percentage removal of TDS is 68%, and a small decrease in pH value about 5%. The generation rates of grey water are mostly influenced by lifestyle and climatic conditions. Contaminants found in grey water are largely associated with the type of detergent used and influenced by other household practices. It is recommended to applied the Restricted irrigation that means irrigation of all types of crops with treated grey water except vegetables and plants including edible parts that can get in direct contact with irrigation water wither these parts are eaten raw or cooked. Keywords: Grey water, Total suspended solid, Chemical oxygen demand COD, biochemical oxygen demands BOD5, inorganic compounds, pH.
معالجة المياه الرمادية- على المستوى المنزلي- في منطقة إربد شمال المملكة الأردنية الهاشمية
وفاء أحمد بخيت
قسم إشراف الأغوار الشمالية || وزارة التربية والتعليم || المملكة الأردنية الهاشمية
Tab title
من وسائل تلبية الاحتياجات المائية في مناطق الشح إعادة استعمال ”المياه الرمادية” التي تتولد على المستوى المنزلي. وهذه هي المياه المبتذلة التي تخرج من بواليع المطبخ وأحواض الاستحمام وغسالات الملابس والصحون. أما المياه المبتذلة التي تخرج من المراحيض فهي ”مياه سوداء”. تهدف هده الدراسة إلى معالجة المياه الرمادية – على المستوى المنزلي- في عينة عشوائية مكونة من 5 منازل في منطقة إربد شمال المملكة الأردنية الهاشمية باستخدام فلتر مكون من مواد طبيعية – الرمل والحصى مرتبة عموديا في برميل بحيث تمر المياه من خلاله. وبعد إجراء التجارب المخبرية على عينات المياه الرمادية قبل وبعد المعالجة، تم ملاحظة وجود انخفاض الأكسجين المستهلك حيويا BOD5 بنسبة37.5 %، والأكسجين المستهلك كيميائيا COD بنسبة 10% أما المواد الصلبة الذائبة نقصت TDS بنسبة 69% أما الحموضة pH انخفضت بنسبة 5%. تتأثر معظم معدلات توليد المياه الرمادية بأسلوب الحياة والظروف الجوية. ترتبط الملوثات الموجودة في المياه الرمادية إلى حد كبير بنوع المنظفات المستخدمة وتتأثر بالممارسات المنزلية الأخرى. لا يفضل استعمال المياه الرمادية في ري الخضراوات التي تؤكل ثمارها وأوراقها نيئة وذلك لتجنب انتقال بعض المواد القادمة من المنظفات اليها، فيما يعتبر ري الأشجار بهذه المياه فضل بكثير بسبب نظام التنقية الذاتي الذي تتميز به الأشجار، وفي حال الاضطرار لري الخضراوات يجب غسل إنتاجها من الثمار والأوراق بصورة جيدة عدة مرات. الكلمات المفتاحية: المياه الرمادية، الأكسجين المستهلك حيويا BOD5 ، الاكسجين المستهلك كيميائيا COD ، مجموع المواد الصلبة TDS، الحموضة والقاعدية pH.